Working Process of API 350HP Oilfield Drilling Triplex Mud Pump
API 350HP Oilfield Drilling Triplex Mud Pump is a high-pressure and high-flow mud pump widely used in the process of oilfield drilling. Its working principle is based on the continuous movement of three pistons to circulate drilling fluid (mud). Below is the working process of the API 350HP oilfield drilling triplex mud pump:
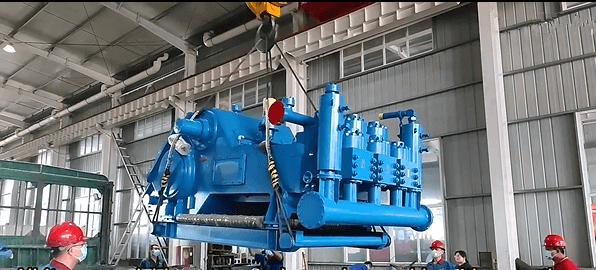
Suction Stage:
The first stage of the working process is the suction stage. During this stage, the piston moves backward from the pump's inlet, reducing the pressure inside the pump, and the suction valve opens. At this time, mud is drawn into the pump from the drilling wellbore or mud pit. The backward movement of the piston creates a negative pressure environment, causing the drilling fluid to enter the pump.
Discharge Stage:
As the piston continues to move forward, the suction valve closes, and the discharge valve opens. This increases the pressure inside the pump and pushes the drilling fluid out of the pump's outlet. During the discharge stage, the mud is expelled from the pump's outlet.
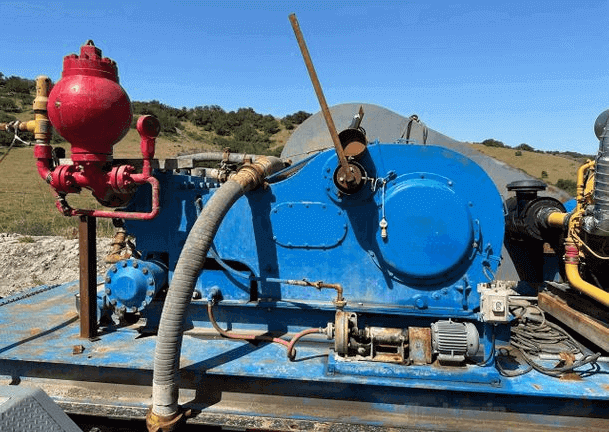
Circulation Effect:
The working principle of the API 350HP oilfield drilling triplex mud pump relies on the continuous movement of three pistons. During the suction stage, drilling fluid is drawn into the pump, and during the discharge stage, drilling fluid is pushed out of the pump. This circulation effect allows the mud pump to continuously provide a stable supply of drilling fluid. The drilling fluid circulates through pumping, carrying drill cuttings from the bottom of the wellbore back to the surface, while cooling the drill bit and stabilizing the wellbore.
Power Source:
The API 350HP oilfield drilling triplex mud pump is typically driven by a powerful engine, usually a diesel engine, to provide the required power. The engine transfers power to the pump's crankshaft through a transmission device, driving the movement of the three pistons.
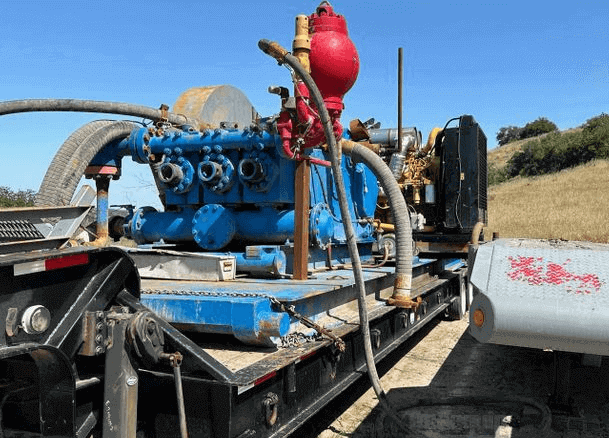
The working process of the API 350HP Oilfield Drilling Triplex Mud Pump involves the continuous movement of three pistons to circulate drilling fluid. During the suction stage, drilling fluid is drawn into the pump, and during the discharge stage, drilling fluid is pushed out of the pump. This continuous circulation ensures a stable supply of drilling fluid, effectively supporting the progress of drilling operations.



