Description
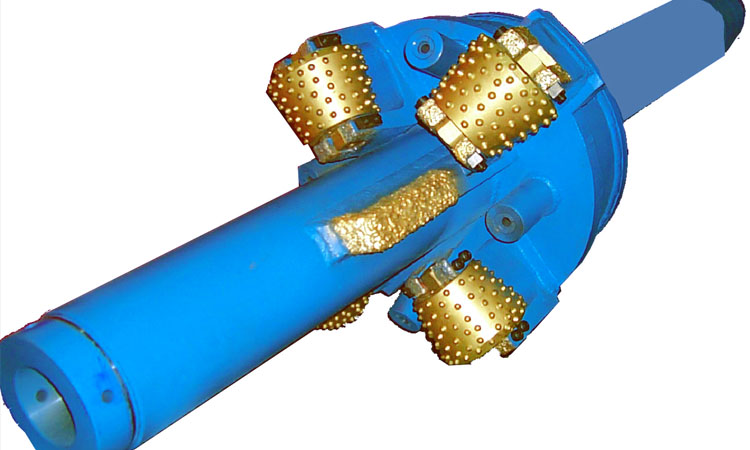
Overview of Casing Scrapers
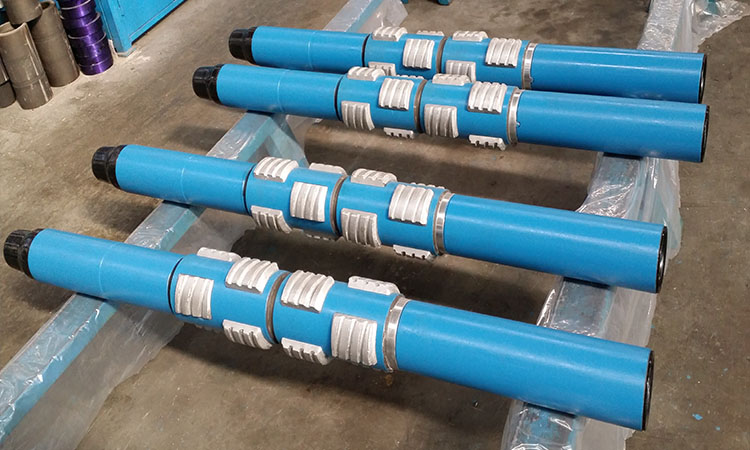
The Oilfield Rotating Casing Scrapers can be used to remove cement block, cement sheath, hard wax, various salt crystals and deposits, perforation burrs and iron oxide produced after casing corrosion on the inner wall of the casing, so that it can be unimpeded Various downhole tools are put into the ground. Especially when the annular space between the running tool and the inner wall of the casing is small, the next step of construction should be carried out after sufficient scraping. The use of casing scrapers has become an essential process in oilfield and oil-water well construction operations, the purpose of which is to improve the success rate of tool running and operation (such as the success rate of packer setting, etc.).
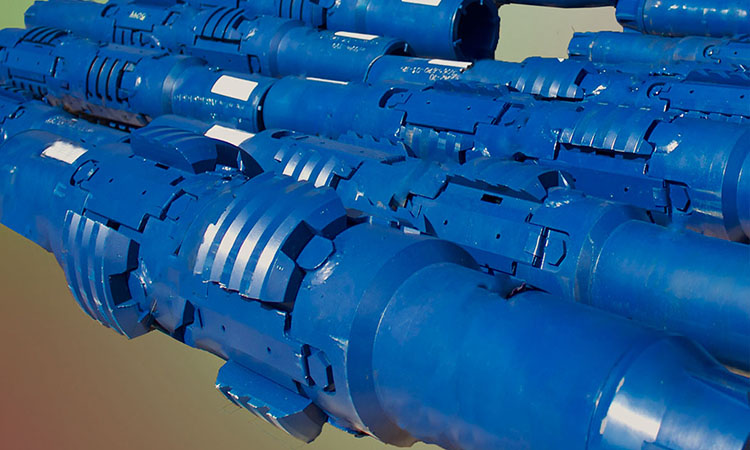
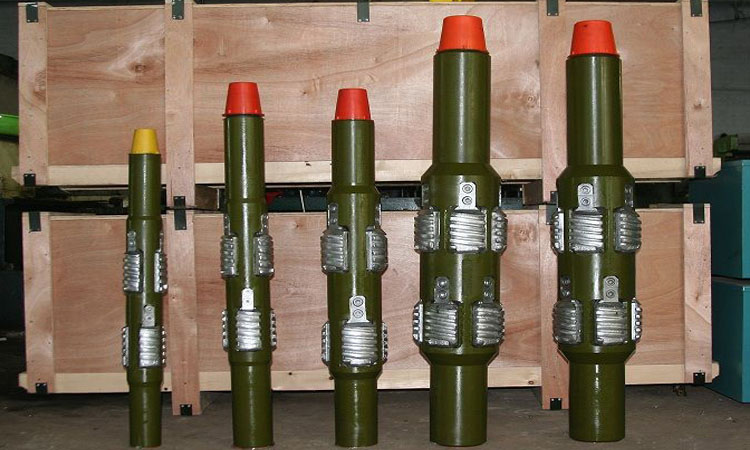
There are three types of casing scrapers: anti-off casing scraper, rubber tube type casing scraper and spring type casing scraper. The anti-off casing scraper is composed of a main body, left and right rotating blades, springs, retaining rings, screws, blade seats, etc. The rubber sleeve casing scraper is composed of an upper joint, a blade, a rubber sleeve, a flushing tube, a lower joint, a shell, and a sealing ring. Spring casing scraper is mainly composed of shell (body), blade, pressure plate, screw, spring and other parts. The housing holds all parts. The upper end and the lower end have inner and outer drill pipe joint threads connected with tools such as drill pipes. In the middle section with the largest diameter, there are two rows of upper and lower alternately milling six large square grooves, and two symmetrical small square grooves at both ends of each large square groove are used to install blades, springs and pressure plates. The casing has water holes from top to bottom to circulate mud. One side of the blade is an arc-shaped surface with spiral grooves and service-shaped blades, and there are tapers at both ends to make the blade pass through each casing collar smoothly. Two lugs at the end of the cone define the dimensions of the scraper in its free state by means of pressure plates. There are four spring holes on the other side of the blade, and the reaction force of the compressed coil spring is the source of the radial feed force during scraping. The blade in the large square groove of the housing should be able to move freely up and down in the groove after being installed.
After the casing scraper is assembled, the outer diameter of the free extension of the blade and the knife plate is 2-10mm larger than the inner diameter of the scraped casing. When going into the well, the blade retracts the rubber tube or the spring barrel inwardly, and at this time, the maximum outer diameter is smaller than the inner diameter of the casing, so it can go down well smoothly. After entering the well, under the action of the elastic force of the rubber tube or spring, the blade and the cutting board move down close to the inner wall of the casing to cut the inner wall of the casing. Every reciprocating action cuts and scrapes the inner wall of the casing once, so that the purpose of scraping the casing can be achieved by reciprocating many times.
Casing Scraping Construction Steps
1. Select the appropriate casing scraper according to the inside diameter of the casing.
2. Connect the casing scraper to the bottom of the pipe string. When conditions permit, the lower end of the scraper can be connected to the tailpipe to increase the weight when entering the well, so as to compress and gather the blades and blades.
3. Operate smoothly when lowering the pipe string, and control the speed of the lower pipe string to 30 pieces/h. When descending to the first 50m of the scraping section required by the design, the descending speed is controlled at about 5m/min. Start the pump cycle at 1-5m above the designed scraping well section. After the cycle is normal, slowly lower the pipe string while slowly rotating it in the direction of thread fastening, and then lift the pipe string repeatedly to scrape repeatedly. When the hanging weight is normal, continue to lower the pipe string .
4. If encountering obstacles in the middle, when the suspended weight drops 20-30KN, stop lowering the pipe string, and do not drop it hard. While cleaning the well, the pipe string should be rotated and scraped repeatedly until the suspension weight is normal, and then the pipe string should be lowered, generally scraping the pipe to 10m below the perforated section.
5. After the scraping is completed, the well should be flushed with large displacement and reverse circulation for more than one week to wash the scraped dirt out of the ground.
6. After the well flushing is completed, pull out all the scraping strings in the well, and the scraping operation ends.
Casing Scraping Operation Requirements
1. Select the appropriate Casing Scraper. When scraping the casing, to prevent the scraper from rotating the shackle in the direction of the blade, it is better to choose a scraper with the blades arranged in different directions.
2. Before the casing scraper goes into the well, it should be carefully checked whether its external dimensions (outer diameter, length, blade elongation) can meet the scraping requirements, so as to ensure the scraping quality.
3. The scraping column should be lowered smoothly. Under normal circumstances, the scraping column is lowered by its own weight and the scraper is pressurized for scraping. If you encounter resistance during the scraping process, you should gradually increase the pressure. Generally, the pressure is 10-20KN, and the maximum pressure should not exceed 30KN.
4. When scraping the perforated well section, there must be a special person to direct the pump to circulate at 2m above the designed scraped well section. After the circulation is normal, slowly lower the pipe string while slowly rotating it in the direction of thread fastening, and then lift the pipe string Repeat the scraping several times until the hanging weight is normal before continuing to lower the pipe string.
5. Scraping times: generally scrape once at the non-perforated part, and the scraping times at the seat seal position should meet the design requirements; lift and lower the perforated position and scrape three times, no resistance, normal hanging weight is qualified (or the number of scraping times reaches Design requirements).
6. Scraping and flushing: In general, after scraping to the design depth, it is required to fully wash the well with a large displacement to clean the dirt in the well. In addition, during the scraping process of many wells, the well-washing plan is formulated according to the specific situation, and the well-washing method can be used in stages. For example, when scraping, above the liquid level, wash the well with reverse circulation every 500m; below the liquid level, wash the well with reverse circulation every 1000m; scraping is prohibited in the casing deformation and sand discharge section.
Precautions for Casing Scraper Scraping operation
1. Both the running tool and the pipe string should pass the ground inspection.
2. It is strictly forbidden to flush sand with a pipe string with a scraper.
3. During the scraping process, attention must be paid to the change of the suspended weight, and the maximum drop of the suspended weight shall not exceed 30KN.
4. After the casing scraper is used once, it is necessary to repair the blade in time, check the spring, and keep the casing scraper in good condition.
5. When scraping the casing, prevent the casing scraper from rotating the shackle in the direction of the blade.
Casing Scraper Scraping Maintenance
1. Remove dirt and disassemble the casing scraper to be repaired into its parts.
2. Check the condition of the shell, spring, and blade, whether the outer diameter and length of the joint meet the specified requirements, and non-destructive testing of the thread.
3. Repair the deformation and damage of the joint thread, shell, etc., and replace the damaged and deformed parts.
4. Reassemble each thread and parts after oiling, and check whether the maximum outer diameter of the blade reaches the specification in the table, whether the blade can be stretched freely, and the return spring is strong.
5. Paint the exterior, apply anti-rust oil to the threads and wear protective wires, and store them in a dry and ventilated place.
The difference between drilling and scraping
1. The main purpose of drilling the well is to inspect the inner diameter of the casing to see if large-diameter tools are allowed to pass through.
2. The purpose of scraping is to remove the debris on the inner wall of the casing.
3. The steel outer diameter of the casing scraper is smaller than the outer diameter of the well gauge, and the well gauge may not pass through the scraped well section, so the casing scraper cannot replace the well gauge.
4. When conditions permit, the casing scraper and the well gauge can be lowered at the same time, and the well drilling and scraping can be completed at one time.
Features of Casing Scrapers
The casing scraper works in a fixed size casing space, so the adhesion on the inner diameter smaller than this size can be scraped off. This kind of scraping function is like a cylindrical reamer in mechanical processing, which uses a tough blade to cut off the cut material and smooth the cut surface. However, because the casing scraper works in a few thousand meters underground, the working environment is a small space, so it has its special working method. The maximum installation size of the casing scraper blade that has not entered the well is larger than the inner diameter of the casing. After entering the well, the blade must be pressed down and retracted by the spring. In addition, when scraping hard materials, it is impossible to scrape all to the inner diameter of the casing at one time, and it must be scraped several times. The inner diameter of the casing increases once each scraping, and the radial feed force is provided by the spring. The casing scraper is connected to the lower end of the downhole pipe string, and the up and down movement of the pipe string is the axial feed during the scraping process. Secondly, it can be seen from the structure of the blade that the blade of each spiral blade has two arc-shaped cutting edges, the inner and the outer. The margin surface, this larger area of the margin still has the effect of grinding and cutting the scraped cut surface during the up and down movement of the blade.
Applications of Casing Scrapers
The purpose of the casing scraper is to remove the cement block, hardened drilling fluid, wax, sand, scale, burr, etc. in the casing, and create conditions for perforating, testing, sealing, and prolonging the production time of the production well.
Price of Casing Scrapers
The Casing Scrapers Price will change randomly with factors such as production cost, transportation cost, international situation, exchange rate, market supply and demand of raw materials. Sino Mechanical aims to provide you with high quality and best price Casing Scrapers. If you are looking for Casing Scrapers, please kindly contact us to get the latest Casing Scrapers price.
Casing Scrapers Supplier
Sino Mechanical, as a Casing Scrapers manufacturer, has more than 20 years extensive experiences in the performance, application and cost-effective manufacturing of Casing Scrapers. We are global Casing Scrapers supplier. We offer a wide range of drilling equipment and have Casing Scrapers for sale. We also provide OEM services. We design, manufacture, and sell Casing Scrapers for your drilling applications. If you want to know latest Casing Scrapers price, don’t hesitate to contact us anytime. We will get back to you within 24 hours.
Specification
Technical Specifications of Casing Scrapers
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR CASING SCRAPER | |||||
CASING SIZE | CONNECTION | BODY O.D. | LENGTH L | BODY I.D. | QTY OF BLADES |
4-1/2 (92-112) | 2-3/8REG | 3-5/8(92) | 35-1/2(895) | 3/4(20) | 2×3 |
5 (95-118) | NC26 | 3-5/7(94) | 35-1/2(895) | 3/4(20) | 2×3 |
5-1/2 (110-133) | NC31 | 4-3/8(110) | 39-5/8(1010) | 1(25) | 2×3 |
6-5/8 (136-162) | 3-1/2REG | 5-3/8(136) | 39-5/8(1010) | 1-3/16(30) | 2×3 |
7 (142-168) | 3-1/2REG | 5-3/8(136) | 39-5/8(1010) | 1-3/16(30) | 2×3 |
9-5/8 (209-235) | 4-1/2REG | 8(203) | 47-3/4(1212) | 2-1/4(57) | 2×5 |
10-3/4 (260-240) | 6-5/8REG | 9(228) | 59(1500) | 2-1/4(57) | 2×5 |
13-3/8 (290-330) | 6-5/8REG | 11-1/4(286) | 54(1372) | 2-7/7(71) | |